Managing Economy in a Time of Uncertainty, a special Weekly Edition
Intelligence and Insights on China's government actions, foreign policy, economy and the capital market.
Letter from the Editor
The US public debate for the moment can hardly go beyond the coming 10 days of the Trump administration. China continues to frame its policy-setting towards long-term outcomes.
Growth paralysis pains the most powerful nation in the world. Growth Engineering (ensured by order) tops the Chinese policy agenda.
China continues to adopt its policy priorities laid out in the 14th Five-year Plan, undeterred and uninterrupted, thanks to calm and order in 2021.
China’s domestic policymakers posit the Chinese economy is to grow circa 8.5% in 2021, a growth rate China has not seen in a decade. The new growth model aims to unleash the power of consumption, the rise of the capital markets, and exercise more risk control over technology and finance. The opening week of 2021 witnesses policies across all three spectrums.
Geopolitical uncertainties abound, epitomized this week by the dramatic turns of decisions over Chinese companies’ delistings, big and small, from the US exchanges.
In times of uncertainty, stability matters. For the moment, let’s relish some measures of discipline and predictability.
Please feel free to share. If you are not a full subscriber yet, please subscribe and join us for a full year of in-depth research and insights on China.
We can only grow with your support. Thank you.
Macro
1. China Lowers 2019 GDP Growth to 6.0%, a Lower Base for 2020 Growth.
China revised its official GDP growth rate for 2019 to 6%, down from 6.1% in its preliminary reading. The estimate for the manufacturing output is down 0.4%, and for the services output is up 0.4%. GDP was $67 billion (435 billion yuan), smaller than the initial estimate. This adjustment would lower the base for this year’s growth rate, which is expected at around 2%. (read more)
Forecasts for 2021
Last week, the World Bank predicted China’s GDP growth to rise from 2% in 2020 to 7.9% in 2021, as consumption and investment recovered rapidly.
Earlier in December, Fitch Ratings upgraded its forecast for China’s GDP growth to 8% in 2021, up from the 7.7% forecast in September, due to recoveries in domestic demand and expectations for coronavirus vaccine deployment.
Twelve domestic securities companies predict an average of 9.13% GDP growth for 2021.
According to China Economic Blueprint 2021, China’s GDP is expected to grow at 7.8%. Total retail sales of consumer goods are expected to grow by 4% to 5% in 2021, indicating that consumption recovery will lag behind China's broader economic recovery in 2021. The 2021 recovery will continue to be led primarily by infrastructure stimulus, with trade remaining uncertain.
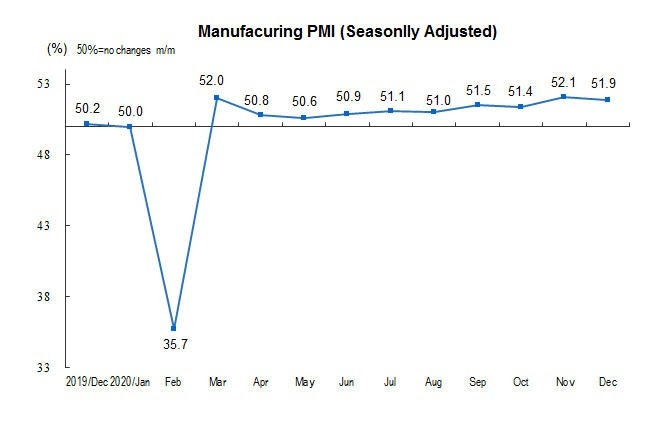
2. China’s PMI Above 50% Threshold for 10 Consecutive Months
In December 2020, China's Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) was 51.9%, down by 0.2% from November, and was above the 50% threshold for ten consecutive months. The manufacturing industry continued to recover steadily and at a slower pace.
Production index was 54.2%, down by 0.5%. The new orders index was 53.6%, down by 0.3%.
This indicates the growth rate of manufacturing production has slightly slowed down.
The narrowing difference between the new orders index and the production index indicates that production continued to be supported by the recovering demand.
The PMI of small enterprises was 48.8%, 1.3% lower than last month, lower than the threshold.
Small enterprises suffer more pressure from higher raw material costs, logistics cost, and labor cost. (read more in Chinese)
The current economic recovery bias obviously over large companies. under pressure to stabilize employment and the market, macro policies will continue to stimulate small and micro-businesses' needs. (read more in Chinese)
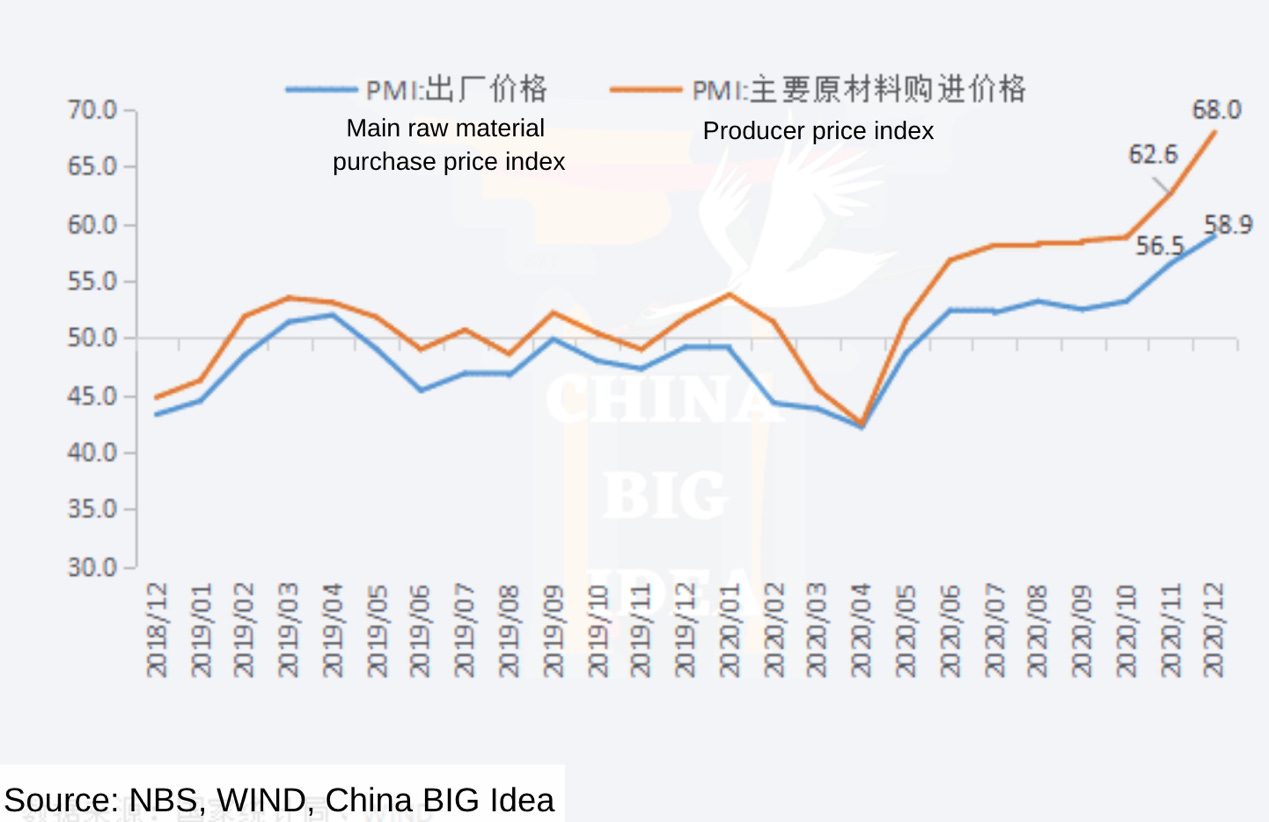
The raw material purchase price index has seen a sharp rise in the last quarter of 2020. Raw material price index has come to a territory that has not been since for the past 2 years.
The PMI in January and the MoM growth rate of the industrial value add will be the core indicators for the momentum of economic recoveries in 2021 and will guide the fine-tuning of China’s macro policy.
3. Boost Consumption on Cross-Ministerial Agenda
On January 5th, the Ministry of Commerce and 12 other departments have issued a joint notice (《关于提振大宗消费重点消费促进释放农村消费潜力若干措施的通知》) on boosting rural mass consumption and the consumption in the key sectors.
The Notice puts out the following 5 critical tasks.
Stabilize and to expand automobile consumption (稳定和扩大汽车消费).
To provide subsidies to the rural residents to facilitate their purchases of new trucks or private cars that can pass the Co2 emissions standards.
Improve the car usage conditions, and to promote the development of the infrastructures.
To optimize the car management and their services.
Promote the consumption of home appliances, furniture, and home furnishing (促进家电家具家装消费)
to encourage the replacement and renewal of home appliances and furniture and provide subsidies for the purchase of green and intelligent home appliances and furniture.
to support the construction of a recycling system for waste materials
Boost food and beverages consumption (提振餐饮消费)
to improve the relevant support policies to promote the development of green catering
Improve the weakness in the rural consumption value chain (补齐农村消费短板弱项)
to improve the rural distribution system, expand consumption in counties and townships, speed up logistics, and expand e-commerce channels for rural agricultural products.
to accelerate the development of rural life services, and support the construction of a living consumption service complex based in the countryside
to optimize the rural consumption environment
Strengthen the policy support (强化政策保障)
to improve the policies and the measures as benefit the enterprises.
to increase the financial support to market players in the circulation industry, especially SMEs and individual businesses
The Importance of Consumption to the Domestic Economic Cycle
The Ministry of Commerce said, “we will stimulate domestic demand, drive up consumption potential, build a modern economic circulation system, clear obstacles to domestic circulation and eventually form a strong domestic market.” (read more)
"According to our estimates, consumption will contribute about 6 % of China's GDP growth, which is likely to reach 8.2% this year," said Liu Ligang, managing director and chief China economist at Citigroup. (read more)
The Focus on the Retail Consumption
The notice focuses on the “big items” of retail consumption, including automobiles, home appliances, and furniture.
The Focus on Rural Consumption
As of May 2020, China's permanent urban population has exceeded 60% of the Chinese population. This indicates that nearly 40% of the population are still rural residents.
In the recent three years, the annual YoY growth rate of total retail sales of consumer goods in the rural areas has risen even more robustly (a 1% more in terms of relative progression) than the growth rate in the urban areas.
In addition, the per capita disposable income of the rural residents grew by 2.2% faster than that of the urban residents, as the relative income gap between urban and rural residents has been continuously narrowing.
In this regard, economist Fu Yifu has recently pointed out that the weakness of consumption continues to be on the supply side, namely the lack of high-quality goods and services, particularly in the rural areas. The full release of rural residents’ consumption potential, he argues, would be conducive to the smoothing of the economic cycle, given their large population. (read more in Chinese)
4. China’s Foreign Currency Reserve Stroke an Uptick
Chinese foreign currency reserve as of the end of 2020 reached $3.2 Trillion, up 1.2% from November. $3 Trillion is conventionally considered by Chinese policymakers as the safety line.
Several factors have attributed to the year-end uptick:
Non-US currency and asset valuation have been inflated due to the depreciation of the US Dollar. On balance, the currency fluctuation contributed to the rise of the foreign currency reserve in US Dollar terms.
China has been acting as the manufacturer of last resort while other trading economies suffer from supply chain disruptions. Enhanced exports of goods have contributed to China’s foreign currency reserve.
What’s Ahead?
None of these factors reflect structural changes. China’s foreign currency reserve still hovers around the $3 Trillion mark. China’s current account surplus will narrow as China turns itself into a bigger import nation. As the rest of the global economies resume full manufacturing capacities, some sectors of Chinese exports will likely decline from its current global weighting.
Policy
1. China Passed the Amended National Defense Law
The Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress ( China’s legislature) approved the amended National Defense Law on December 26, 2020.
Key amendments:
National security has been given an enhanced meaning. Development interest is added, along with national unity, territorial integrity, and state safety, to the definition of national defense.
中华人民共和国的主权、统一、领土完整、安全和发展利益遭受威胁时,国家依照宪法和法律规定,进行全国总动员或者局部动员。
Background
The first Chinese National Defense Law was published in 1997. The Law went through a minor amendment in 2009.
The 2020 amendment encompasses 54 revisions, 6 additions, 3 deletions, and variations to the title of chapters 4 and 5. This represents a comprehensive amendment to the Law.
Key Amendments: (read more)
It is made clear that the military is under the leadership of the Party. The party’s rule over national defense activities is strengthened.
强调国家对国防活动实行统一的领导,武装力量受中国共产党领导。二是完善了国家机构的国防职权。Addition: Chairman of the Central Military Commission is the absolute commander-in-chief according to the constitution.
根据宪法的规定,新增“中央军事委员会实行主席负责制”的内容。
The scope of national defense activities has been enlarged. The original scope of “ border security, coastal security, and aerial security” is expanded to “border security, coastal security, aerial security, and defense of other areas of strategic security.” Other strategic areas include activities and interests in outer space, electromagnetic fields, and cyberspace.
“国家采取必要的措施,维护在太空、电磁、网络空间等其他重大安全领域的活动、资产和其他利益的安全”等内容。
The portion on defense R&D and military procurement is amended. Innovation and self-reliance are included in the national defense policy. The use of a whole-of-society approach in pulling resources to expedite R&D is highlighted.
将“创新驱动、自主可控”纳入国防科研生产方针;新增“国家充分利用全社会优势资源”“加快技术自主研发”.
The component on the national defense budget and national defense resource management is amended. The amended law states that a legislative budgetary process will approve national defense expenditure. This change brings the procedure similar to the practice in the US. The previous Chinese national defense expenditure falls under a fiscal allocation process.
R&D owned by the national defense can be permitted for other use ( non-military use) after the national defense priorities have been satisfied.
“国防资产中的技术成果,在坚持国防优先、确保安全的前提下,可以根据国家有关规定用于其他用途”等内容。
Strengthened the protection of the rights of the armed forces. Armed forces must be loyal to the Communist Party of China.
Military service is ensured as the admired profession by society. This reflects a revision from the previous wording that the armed services are the society's respected profession.
Amended the law on international military relations. The Law safeguards the global system under the UN and international order based on international law.
Armed forces can be mobilized overseas to protect Chinese citizens, organizations, institutions, and facilities by law.
New items in China’s national defense Law
For the first time, a defensive national defense strategy is written into the Law.
China carries a full society mobilization in national defense and pan society education on national defense.
Ant Group under Domestic Scrutiny
Ant Group’s business is under antitrust review and regulatory scrutiny since the dramatic halt of its IPOs on November 4.
Global headlines swirled about the “disappearance” of Jack Ma from the African talent show that he has created. Since he gave the Bund Summit speech in early November, it has been more than two months since his last public appearance. However, any conspiracy theory around him should be cautioned.
Ant’s fate remains uncertain.
The analysis is only available to subscribers in Thursday’s issue.
Industry
1. China to cut subsidies on EVs by 20% in 2021
In 2021, China will cut subsidies on electric vehicles by 20%, according to the notice from the Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, and National Development and Reform Commission. The subsidies will apply to passenger cars priced at less than 300,000 yuan.
Subsidies on NEVs for public transport will be reduced by 10%.
2021年,新能源汽车补贴标准在2020年基础上退坡20%;为推动公共交通等领域车辆电动化,城市公交、道路客运、出租(含网约车)、环卫、城市物流配送、邮政快递、民航机场以及党政机关公务领域符合要求的车辆,补贴标准在2020年基础上退坡10%。
In April, the Ministry of Finance announced that China would extend its subsidy scheme for new energy vehicles (NEVs) to the end of 2022. The subsidies will reduce by 10%, 20%, and 30% respectively in 2020, 2021, and 2022. (read more in Chinese)
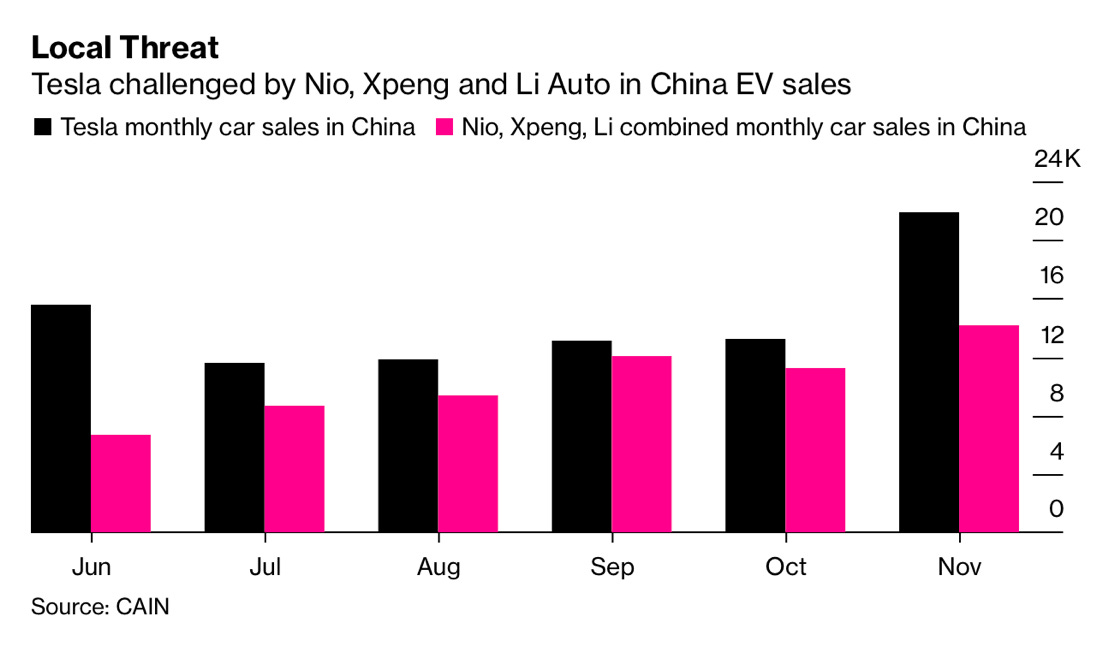
On January 1, locally produced Tesla Model Y made its debut in China. The Model Y Dual motor AWD variant would start at 339,900 yuan ($52,000), down by 148,100 yuan from its pre-sale price. The Model Y Performance now starts at 369,900 yuan ($56,600), down by 165,100 yuan. Sales prices are lower than those in the US and lower than expectations, causing competitive pressure to domestic EV brands, including Li Auto (ONE), Xpeng, and NIO. (read more in Chinese)
The Chinese trio saw a steady rise in sales in 2020. (read more)
2020’s Railway Investment Reached 110% Target
In 2020, China completed 781.9 billion yuan ($119.56 billion) of fixed asset investment in the railway sector, 71.9 billion yuan ($11.3 billion) more than the goal set at the beginning of the year.
High-speed Rail Outlook for 2021
In 2019, China ranked 1st in high-speed rail operating mileage, 10 times longer than the second-highest-ranking Spain. The other countries in the top 5 list are Japan, France, and Germany.
The national railway sector completed 2.16 billion passenger trips in 2020, and the figure is expected to reach 3.11 billion in 2021, a spike of 43.7% YoY.
It is also expected that the sector will transport 3.7 billion tonnes of freight in 2021, an increase of 3.4% YoY.
China's railways are set to expand by about 3,700 kilometers in 2021. The Sichuan-Tibet Railway and other key national projects are high on the 2021 infrastructure list.
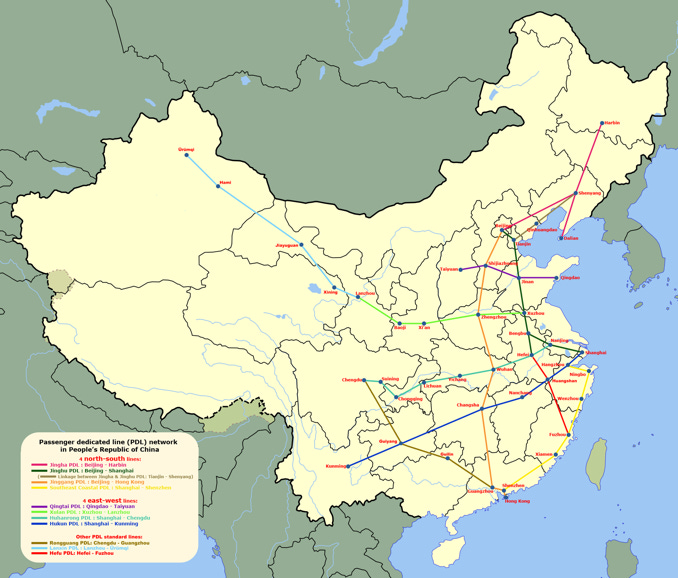
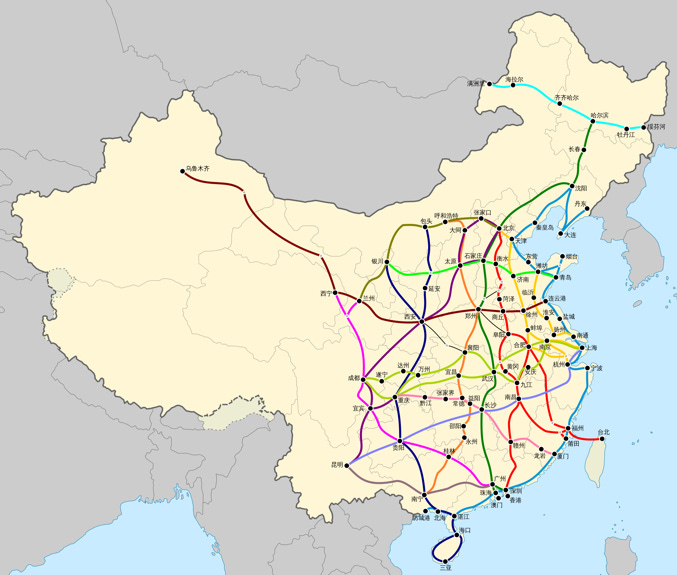
From 4X4 to 8x8 Railway Coverage
The “Four Vertical (north-south) and Four Horizontal (east-west)” (4+4) high-speed rail (HSR) network has been completed ahead of time, while the “Eight Vertical and Eight Horizontal” (8+8) HSR network will almost double the 4+4 route length is in steady progress.
“‘四纵四横’高铁网提前建成,‘八纵八横’高铁网加密成型。”
Map of the 4+4 HSR Grid
Map of the 8+8 HSR Grid
Number of China-Europe Rail Freight Service Hits New Record
In 2020, 12,400 China-Europe freight trains were carrying 1.135 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU), up 50% and 56%, respectively, on a YoY basis.
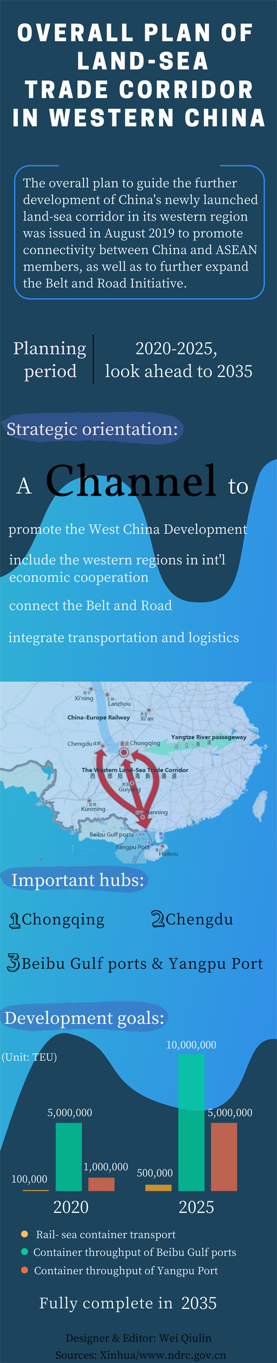
Western Land-Sea Corridor Project is Making New Progress
In 2020, there were 3,600 trains carrying 190,000 TEU, up 73% and 80% respectively year-on-year. The corridor holds strategic importance as it connects the Silk Road Economic Belt, the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road, and the Yangtze River Economic Belt.
According to the overall plan (《西部陆海新通道总体规划》) signed by China’s NDRC in 2019, the project will improve regional logistics and support western China to play a role in the international economic connectivity.
Capital Market
1. Chinese companies IPO in 2020
A-share market
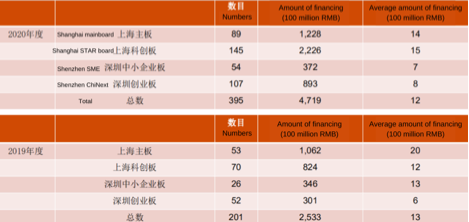
In 2020, both the number of A-share IPOs and the amount of financing increased significantly, compared to 2019. 395 new companies were listed in 2019, with $73.09 billion raised (471.9 billion RMB), hitting a new high since 2011. The number of IPOs and the amount of financing increased by 97% and 86% over 2019, respectively.
The registration-based IPO system, a major capital market reform initiative, has accelerated the speed of A-share listings. The number of IPOs issued through the registration system has exceeded the listing review system. 145 companies were listed on the NASDAQ-like Shanghai STAR Board and 107 IPOs on the Shenzhen ChiNext Board, both of which exceeded the number of 89 IPOs on the Shanghai mainboard.
Source: PwC
Chinese companies listed in the US market
In 2020, 31 companies were listed in the US capital markets, raising a total amount of $12.1 billion, four times the amount Chinese companies raised in 2019.
Chinese corporate listings on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange
Despite adverse factors of the year, Hong Kong's IPO market came second in the total amount of capital raised through IPOs globally.
In 2020, of the 154 new shares listed in Hong Kong, 146 were listed on the HK mainboard, mainly retail consumer goods and services and industrial companies, down 16% from last year. Eight companies are listed on the GEM board, 47% less than last year.
The total financing in the market in 2020 is $51.29 billion (HK $397.7 billion), an increase of 25% over the same period. Mainboard financing reached $51.22 billion (HK $397.1 billion), up 26% year on year on the back of Chinese digital and technology company listings. GEM's new listing raised $77 million (HK $600 million), down 40% over the same period.
Hong Kong Share Buybacks
In 2020, the overall trading enthusiasm in Hong Kong's capital market was not high.
In 2020, 174 listed companies in Hong Kong had made a share repurchase, with a total repurchase of $2.09 billion (HK $16.19 billion), up 15.4% year on year. The average asset-liability ratio of 174 repurchase enterprises in 2020 is 43.8%, and the average turnover rate of the shares in 2020 was 48%.
Of the 174 listed companies which have made share repurchases, 39 were from the disposable consumption sector, accounting for about 22%, followed by 28 companies from the real estate sector, accounting for about 16%, followed by 27 companies from the IT industry, accounting for about 16%.
From the perspective of investment returns, the medical device gathered strong investment heat in the Hong Kong stock exchange in 2020. As of December 31, the medical equipment sector in HK rose by 90.2%.
In terms of repurchase amount, the “2020 repurchase king” was Evergrande. 46 stock repurchases were made by Evergrande in 2020, with a cumulative repurchase amount of approximately $600.65 million (HK$4,657 million), accounting for approximately 28.7% of the total repurchase on the HKSE.
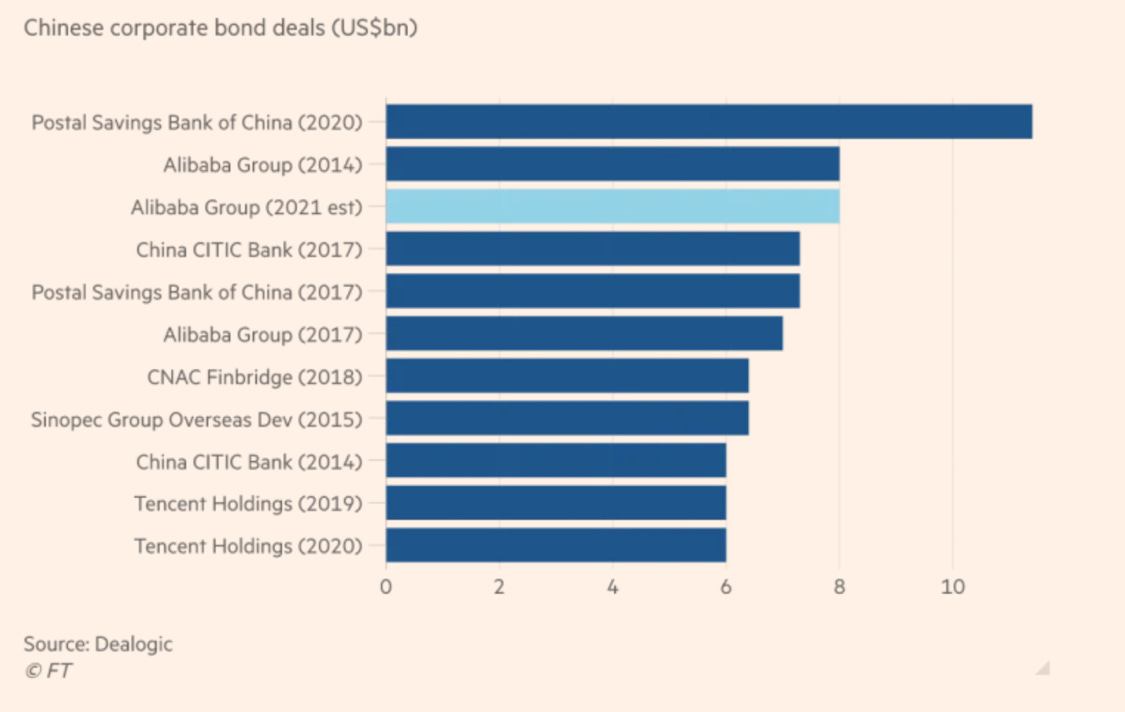
2. Alibaba’s US$8 Billion Debt Financing
Alibaba will raise up to US$8 billion in dollar bonds this month – the funds will be used to invest outside China and to develop its overseas operations. Alibaba plans to issue at least US$5 billion in bonds. However, will the demand be higher, Alibaba could raise up to US$8 billion in total. That would mirror Alibaba’s 2014 record US$8 billion bond offering. In 2017, the E-commerce firm raised an offshore debt of US$7 billion in the form of a bond deal.
As the interest rates have been lowered to stimulate the coronavirus-ravaged economies, Alibaba is set to take advantage of the low-priced debt. So far, in 2021, borrowers have globally sold more than US$65 billion of bonds as the year 2020 established a total record of more than US$3.6 trillion of sold bonds.
Alibaba has also recently announced an increase in the size of its share buyback program from US$6 billion to US$10 billion. The program will run until the end of 2022.
These announcements come at a difficult time for Alibaba. After the delay of Ant Group’s IPO, which was set to be the world’s largest, Alibaba’s Hong Kong-listed shares fell nearly a quarter of their values. Moreover, greater regulatory scrutiny has been placed on Alibaba in recent months, including an antitrust investigation.
However, a well-received bond offering would mark a major sign of confidence in Alibaba, despite its recent troubles.
International Relations
1. China and EU Conclude negotiations for landmark CAI
In a video call on December 30, Chinese and European Union leaders concluded in principle the 7-year marathon negotiation for a bilateral investment deal. The Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (CAI) delivers on commitments made to agree at the end of 2020 and is a major diplomatic win for China.
A statement issued by key leaders in the EU, Charles Michel (President of the European Council) and Ursula von der Leyen (President of the European Commission) states that the Agreement was of “major economic significance and also bound the parties into a values-based investment relationship grounded in sustainable development principles.” EU member states are expected to benefit from the deal as it tackles Chinese policies that have been deemed by Europe to be market-distorting, such as industrial subsidies, state control of enterprises, and forced technology transfers. (read more)
Key components of the Agreement (read more):
Forced technology transfers: Direct prohibition of forced technology transfers and any state interference in technology licensing. The Agreement also addresses the protection of intellectual property and trade secrets.
Market access: rebalance the existing asymmetry and bring China closer to the EU in terms of the level of openness and level playing field, given China's market is far less open than the EU's.
The CAI requires state-owned enterprises to act according to market norms, with no preferential market treatments. This entails measures such as eliminating quantitative restrictions, equity caps, and joint venture requirements, providing new opportunities for access by the EU companies to the Chinese market. This market access level is essentially similar to what the US has achieved in the US-China phase 1 trade deal.
Sustainable development: The Agreement commits both sides to support the environment and labor rights.
Market opening on renewables in the EU is capped at 5% for each EU member state and is contingent on reciprocal openness from China.
Prohibits lowering labor and environmental standards to attract investment
Commits to the implementation of the Paris Accord.
Commits China to the ratification of outstanding ILO fundamental conventions on forced labor. According to the European Commission, China has sent a strong signal in the CAI to ratify the outstanding conventions.
· Dispute settlement: The CAI will include a state-to-state dispute settlement mechanism and an institutional framework for monitoring the implementation of commitments. There will also be an ad hoc mechanism for a fast engagement at a political level in case of urgent issues.
What sectors stand to benefit?
Current bilateral investments between China and the EU concentrate on manufacturing. On the European side, industries such as automobiles, healthcare, R&D in biotechnology, and computer services will likely benefit from eliminated joint venture requirements, improved transparency, and investment liberalization.
For China, industries such as renewable energy, green technology, and digital technologies are expected to benefit. Given multiple EU member states' national security concerns, the European Commission emphasized that sensitive areas such as public services, critical infrastructure, and technologies remain fully preserved.
China’s Official proposal to the EU
According to Xinhua, the below proposals are made for 2021 at the conclusion of the China-EU CAI. (read more)
1. 协调抗疫行动: Coordination in actions to tackle the coronavirus pandemic, especially in the equitable distribution of vaccines to developing countries.
2. 共促经济复苏: Cooperation in post-pandemic economic recovery through policy communication and coordination.
3. 对接发展战: Strengthen connections with EU member states through the One Belt One Road initiative
4. 加快绿色发展: Boost diplomatic efforts at international climate change summits to foster progress in preserving biodiversity and tackling climate change.
5. 推动多边合作: Promote cooperation through multiple institutional channels, such as the UN, G20, WTO, and WHO, to precipitate the resolution of political issues around the world.
What is not in the CAI?
The CAI is not a trade deal. It is merely a bilateral investment treaty that aims to address principally equal market access between China and the EU. It is not as comprehensive as the US-China phase one trade deal, in which trade imbalance is address with specific punitive tariffs and purchase commitments.
What comes next?
In the coming months, it will need the European Parliament's approval. Some have expressed reservations as a result of allegations of human rights violations against Uyghur Muslims and the treatment of the Hong Kong people.
The process of ratification is estimated to take around one year.
China and the EU have also committed to a 2-year deadline to conclude negotiations on an additional investment protection agreement.
2. Chinese Foreign Minister Visits 5 African Countries at the Start of 2021
State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi started his official visits to five African countries, including Nigeria, DRC, Botswana, Tanzania, and Seychelles, on January 4, 2021. This is Wang’s first official overseas visit in 2021. (read more)
Since 1999, Africa has been the destination for Chinese foreign ministers’ first overseas visit each year. (read more)
But this year’s trip is unique as:
The COVID-19 pandemic has pushed Africa into recession, making African countries apply for debt relief from the G20, including China. (read more)
Analysts foresee China will be more cautious and slow down the lending for the belt and road projects. (read more)
The global distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has started. China has promised vaccine access to African countries. (read more)
2021 is the final year for implementing the outcomes of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation Beijing Summit. (read more)
During the visit, Wang Yi will exchange views with African leaders on the next FOCAC meeting preparations. (read more)
Analysts said during Wang’s visit, China’s “vaccine diplomacy” and the need to assure African countries that Beijing will continue to fund the infrastructure projects in Africa will be featured.
Stephen Chan, a professor of politics and international relations at the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London, said the visit “will certainly relate to China’s vaccine diplomacy but is also a snub to countries like Zimbabwe, long expecting Chinese help but without economic discipline.” (read more)
Botswana and DRC, two of the five stops on this trip, are 2 of the 11 African countries that have stayed out of China’s BRI agreements. (read more)