"Two New, One Major" Policy Speeds H2 Economy, Tightens Up Belts, Speeds Up Export Control Law, launches Mars Mission, Kicks-off National Pipeline Co. & Energy Reform, India Phases Out Chinese Apps(w)
Intelligence and Insights on China's government actions, foreign policy, economy, and the capital market.
Today, we closely examine an intensive wave of Government ministries’ policy declarations relating to China’s H2 economic recovery, featuring major policies characterized under the new terminology " Two New, One Major". China tightens up belts, speeds up Export Control Law, launches Mars Mission, kicks-off National Pipeline Co. & Energy Reform. India Phases Out Chinese Apps, and more.
Government in Action:
Government’s “Two New, One Major” (“两新一重”)Leads China’s H2 Economic Recovery.
“两新一重” (“Liang Xin, Yi Zhong”), a key phrase out of this year’s Government Work Report on May 22, clearly frames the government economic direction for H2, 2020.
Two New (两新)refers to new infrastructure, and new urbanization development;
One Major (一重)refers to major transportation and water resources projects.
Ministry of Transportation:
Will plan and develop a series of major nationwide transporation projects, including Sichuan-Tibet Railway, Shenzhen-Zhongshan Bridge.
Shenzhen-Zhongshan Bridge (source)
Ministry of Industry and IT (MIIT): The plan is to empower 100 Chinese cities with“double Gigabit” networks-a mobile 5G Gigabit network, and a fiberoptic Gigabit network. Cities including Chongqing, have launch detailed 2020-2022 working plans to turn the city into a “double Gigabit” city. (read more)
Inner City Duty Free Shopping policies is under feasibility study and may soon be launched. Qualified retail and department stores will be able to apply for inner city duty free licenses.
Chinese overseas shopping will continue to be severely curtailed in H2, 2020. According to Morgan Stanley, the onshoring of Chinese consumption overseas may bring back retail revenue at around 1 trillion RMB ( $145 billion) annually.
What will lead the economic recovery in H2 in China?
It will continue to be led by infrastructure investments and Industrial production.
In looking at the recovery of China’s Small and Micro-sized economies in June, which provided a more market-based indication, manufacturing output surpassed its pre-COVID19 level as of June.
Primary industry recovered to about 95% of its January level. Service industry continues to be the slowest to recover, currently at 80-90% of pre-crisis levels.
In looking at China’s Q2 GDP release, while GDP has not returned to Jan 2020 level, real estate investments already returned to positive growth in Q2, registering 1.9% positive growth year over year. (read more)
China’s industrial production continues to steadily recover through June 2020. Industrial side of the economic recovery will continue to exhibit strength over consumption recovery. (read more)
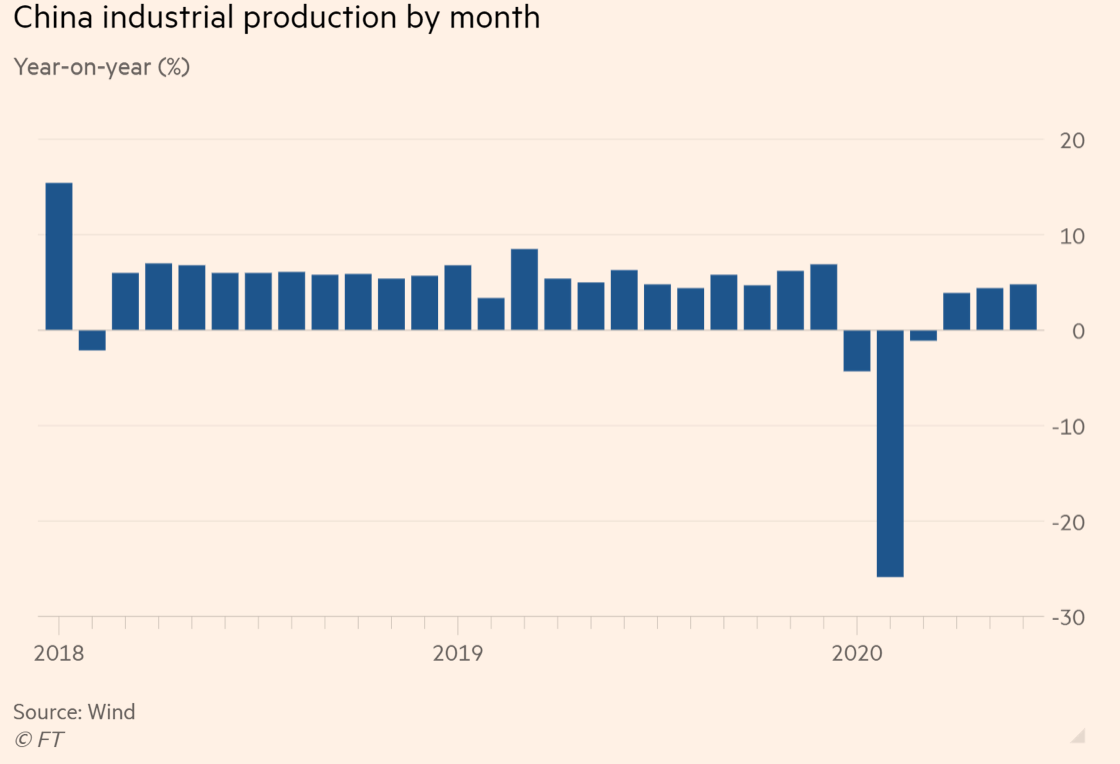
Overall, the supply side recovers more strongly than the demand side so far in the Chinese economy. The pattern should continue in H2 2020, with manufacturing and infrastructure investment leading the recovery, while consumer confidence and employment further normalizes.
2. China Tightens Up Belts at Central Bureaucracies But Keeps Bottom-up Fiscal Expenditure to Sustain Growth and Keep Employment.
Amid swift economic recovery from COVID-19, however, China has tightened restraints on public expenditure by governmental agencies, while keeping intact local expenditure vital for growth and job creation/maintenance at county level. The Chinese Ministry of Finance (counterpart to US Treasury Department) recently quotes this less-reported move in modest details. It demonstrates a higher degree of confidence to tackle issues with good bottom line. (read more)
The Chinese Ministry of Finance cites state media reports with highlights below:
中央部门带头过紧日子
“The central government must take the lead to live with an austere life.”
对县级的转移支付规模只能增、不能减。 (read more)
“Scale of the fiscal transfer cascading to counties must increase without any cut.”
Consequences:
· Chinese Treasury is determined to impose more stringent budgetary restraints on spending using fiscal expenditures.
· Gov’t budget cuts of 50% against “non-mandatory, non-urgent expenses,” except for those duly approved for anti-pandemic and disaster responses.
· Tightened fiscal discipline with calls for “no budget overruns.”
· Stability-driven mindset: keep intact the expenditure at county level to prioritize for keeping economic growth and jobs.
The BIG Read
China Speeds Up Export Control Law with Deeper Policy & Institutional Alignment & Punitive Fines Against Violation. What Does it Entail?
China released on June 28, 2020 the “second-reading” version of the draft 2020 Export Control Law. (read more), along with the draft Data Security Law, which China Bid Idea alerted previously (read more). This validates the pre-existing momentum and newly-reinforced policy tools to potentially retaliate / reciprocate ongoing US extra-territorial enforcement against China. This has significant ramifications shaking up the entire supply chain for any sensitive commodities caught between conflicting US China sanctions in the months to come.
This is against the backdrop of intensifying legislation and sanctions that treats China as the “near rival” under the “whole of government” approach led by US, China also paces up her legislation and administration of its own export control regime.
Unsurprisingly, the “safety and controllability” remains the underlying tone for other “companion” legislation such as the National Security Law and Cyber Security Law. Despite vast ideological difference, the architecture of the Chinese counterparts to US CFIUS and export control laws as the essential components echo and emulate with U.S. “whole-of-government strategy,” with the Chinese-socialist-style, all-nation approach underlying China’s comprehensive yet evolving security surveillance and control regime. (See earlier analysis here).
· Analysis
What’s salient from the US regime and prior version of the Chinese draft Export Control Law demonstrates China’s growing confidence and policy choice for greater transparency, foreign investment protection and attraction and carefully paced “structural reform” in light of critics by trading partners underlying the Phase-1 US-China Trade Agreement, such as the following:
(a) Greater Enforcement and Individual-level Liability. The new Export Control empowers the Chinese Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) with on-site verification and various investigatory powers, along with fines up to 10 times of the “illegal gains” from alleged “unauthorized” exports of controlled items, either domestically or overseas. The “covered persons” under the new Export Control Law’s jurisdiction extends from “citizens, corporations and other organizations” to “individuals and organizations.” Such penalties may extend “aiding and abetting” liabilities against those “providing services” to alleged wrongdoers. Please note this broadly encompasses from those involved in e-commerce services to financing dealers and brokers, as well as the logistics providers, irrespective of contractual agreements otherwise agreed by the parties.
(b) Greater Instructional/Policy Alignment Prepared to Swiftly “Reciprocate” foreign Sanctions: It provides better clarity within the Chinese bureaucracy to sort out turfs and commands local authorities to escalate for vetting the controllability of any controversial item to centralize the licensing process and mitigate local protectionism using export control regime discriminatorily against foreign-invested enterprises.
(c) More Sanction and Entities Lists to Come. It will unify and consolidate the currently fragmented Chinese counterparts of US EAR (Export Administration Regulation). It will also eliminate policy considerations non-essential to “national security” and foreign policy” justifying sanction lists, such as “industrial competitiveness.”
(d) Reinforced Embargo Honoring China’s Treaty Obligations. It reiterates China’s continuous policy for comprehensive embargos already in places to implement resolution reached by the United Nations Security Council, such as those against North Korea, and those against nuclear/bio/chemical-weapon proliferation.
· Outlook
Listed above are key highlights of the latest Chinese developments on export control and public procurement reforms. The new Export Control Law validates the pre-existing momentum and newly-reinforced policy tools to potentially retaliate / reciprocate ongoing US extra-territorial enforcement against China.
This coincidentally responds what US Attorney General William Barr warned on its “China Initiative” that US will further intensify pressing major European-based MNCs as “market alternative” to Chinese national champions like Huawei to comply with US foreign and national security policy priorities and enforcement with “unity.”(read more)
Given the uncertainty cascaded by these increasing conflicting regimes over international businesses, we will be delighted to provide fuller analysis as the Export Control Law evolves and vigorously enforced as “reciprocity” to US-driven sanctions to safety its technology leadership and foreign policy interests.
Chinese Tech
…..( paid subscription only)


